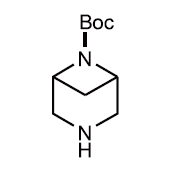
azetidin-3-ol hydrochloride

Product Description
PharmaBlock Sciences (Nanjing), Inc.

-
CN
-
2016On CPHI since
-
3Certificates
-
1000 - 4999Employees
Company types
Primary activities
Categories
Specifications
PharmaBlock Sciences (Nanjing), Inc.

-
CN
-
2016On CPHI since
-
3Certificates
-
1000 - 4999Employees
Company types
Primary activities
More Products from PharmaBlock Sciences (Nanjing), Inc. (17)
-
Product 1-Diphenylmethyl-3-cyanoazetidine
PharmaBlock provides wide range of pharmaceutical products which includes1-Diphenylmethyl-3-cyanoazetidine. Storage:>200kg. Contact us for more information. -
Product 2,4-Dichloro-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine
PharmaBlock provides wide range of pharmaceutical products which includes2,4-Dichloro-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine. Storage:>5kg. Contact us for more information. -
Product 3-methylazetidin-3-ol hydrochloride
3-methylazetidin-3-ol hydrochloride -
Product 3-methylazetidin-3-ol hydrochloride
3-methylazetidin-3-ol hydrochloride -
Product 3,5-Dimethyl-1,2,4-triazole
PharmaBlock provides wide range of pharmaceutical products which includes3,5-Dimethyl-1,2,4-triazole. Storage:>30kg. Contact us for more information. -
Product 5-Bromoindazole
PharmaBlock provides wide range of pharmaceutical products which includes5-Bromoindazole. Storage:>5kg. Contact us for more information. -
Product azetidine-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride
azetidine-3-carbonitrile hydrochloride -
Product cyclopropanol
cyclopropanol -
Product ethyl 2-cyclopropylacetate
ethyl 2-cyclopropylacetate -
Product ethyl 2-cyclopropylacetate
ethyl 2-cyclopropylacetate -
Product methyl 1-formylcyclopropanecarboxylate
methyl 1-formylcyclopropanecarboxylate -
Product Methyl 3-chloropyridazine-6-carboxylate
PharmaBlock provides wide range of pharmaceutical products which includesMethyl 3-chloropyridazine-6-carboxylate. Storage:>10kg. Contact us for more information.
PharmaBlock Sciences (Nanjing), Inc. resources (11)
-
News EcoVadis Silver Medal! PharmaBlock Excels in Sustainability
PharmaBlock Group has been awarded a Silver Medal for sustainability by EcoVadis, ranking us in the top 15% globally! -
News PharmaBlock Receives 2024 ACS CMO Excellence in Green Chemistry Award for Two Consecutive Years
PharmaBlock was awarded the 2023 and 2024 CMO Excellence in Green Chemistry Award by the American Chemical Society (ACS) Green Chemistry Institute Pharmaceutical Roundtable (GCI PR). This esteemed award, marking the company's second consecutive win among global CDMO companies, is a testament to PharmaBlock's persistent commitment to green chemistry and its unwavering efforts in crafting innovative, sustainable solutions for the pharmaceutical industry. -
News PharmaBlock Receives 2023 ACS CMO Excellence in Green Chemistry Award
PharmaBlock has been selected as the winner of the 2023 CMO Excellence in Green Chemistry Award by the American Chemical Society (ACS) Green Chemistry Institute Pharmaceutical Roundtable (GCI PR). This award honors and confirms PharmaBlock’s commitment to green chemistry and its achievement in developing innovative solutions for sustainable development in the pharmaceutical industry. -
Video Manufacturing Site Virtual Tour
360° Virtual Tour of Pharmablock Zhejiang GMP Manufacturing Site is ready to go! The virtual tour will provide you an immersive interactive view of the workshops, analytical labs, and the new Chemistry & Engineering Technology Center. Check the demo video below to have a quick look. Contact our BD representatives or the marketing team (marketing@pharmablock.com) for a full interactive version. -
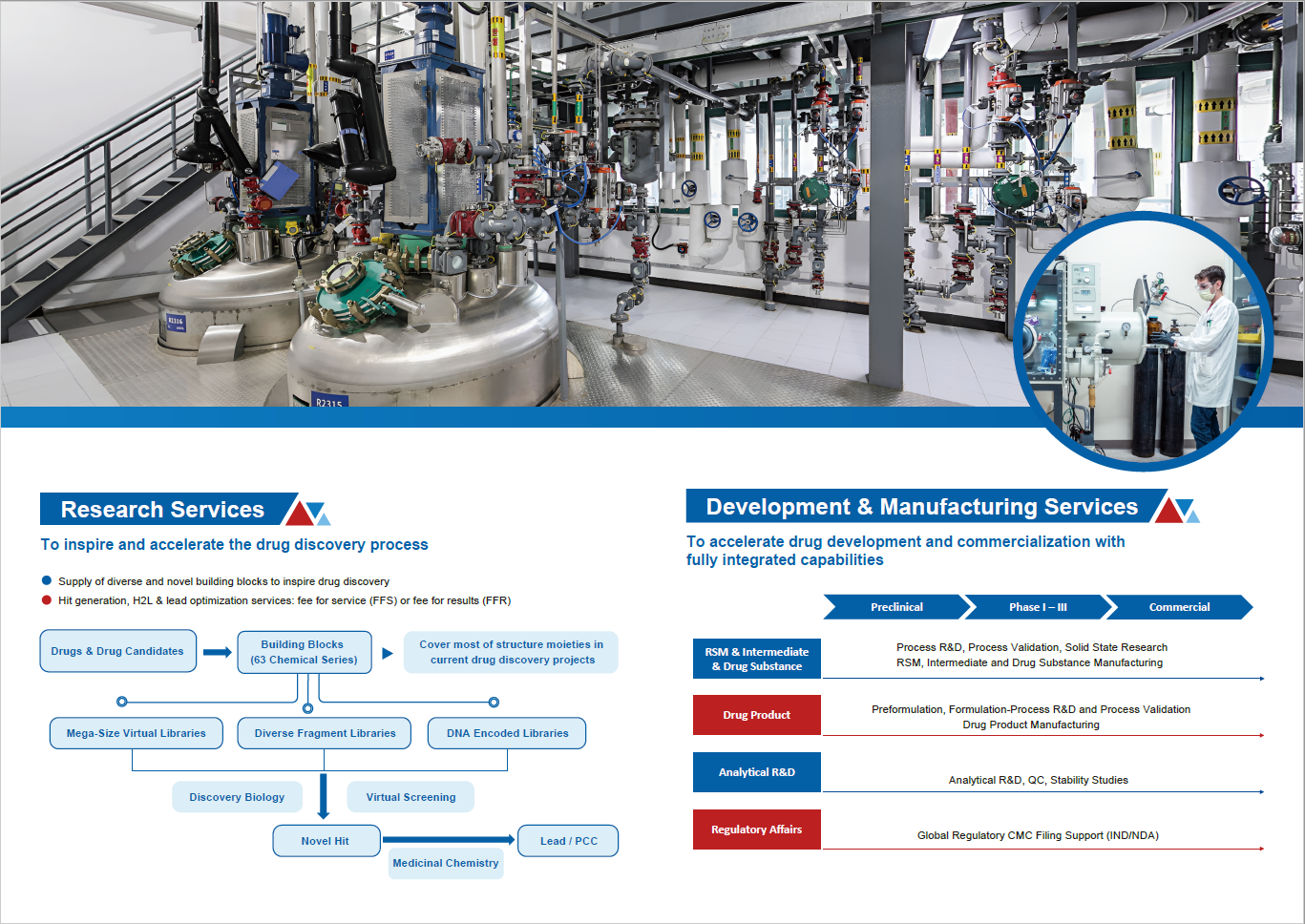
Brochure PharmaBlock CDMO Capabilities and Chemistry & Engineering Technologies
Led by an experienced management and core technical team, PharmaBlock is providing development and manufacturing solutions of intermediates, drug substance for development and commercial stages. Taking full advantage of building blocks availabilities, along with its know-hows in chemistry, process development, analytical development, manufacturing, and engineering technologies, the team has distinguished itself for capabilities to tackle challenging chemistry, secure reliable supply, control cost with full compliance of quality and EHS etc.
-
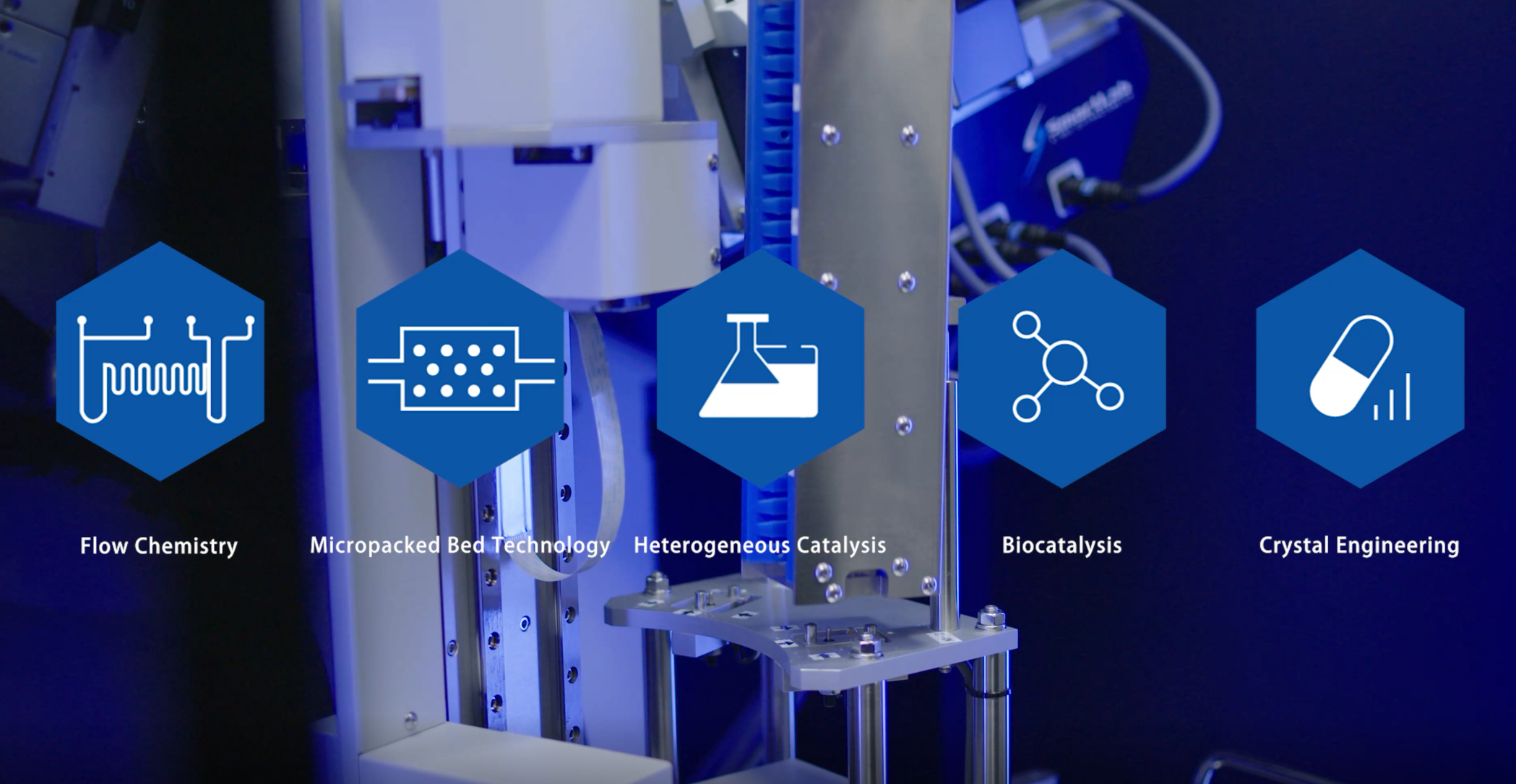
Brochure Chemistry & Engineering Technologies
PharmaBlock has invested in a number of innovative technologies to enable greener, safer, and more efficient process for manufacturing. We have a dedicated chemistry and engineering technology team working closely with experts in process development and manufacturing to implement optimal process solutions from pilot to commercial scale.
Capabilities include: flow chemistry, micropacked bed hydrogenation, biocatalysis, heterogeneous catalysis, solid state chemistry, crystallization, engineering technologies etc. -
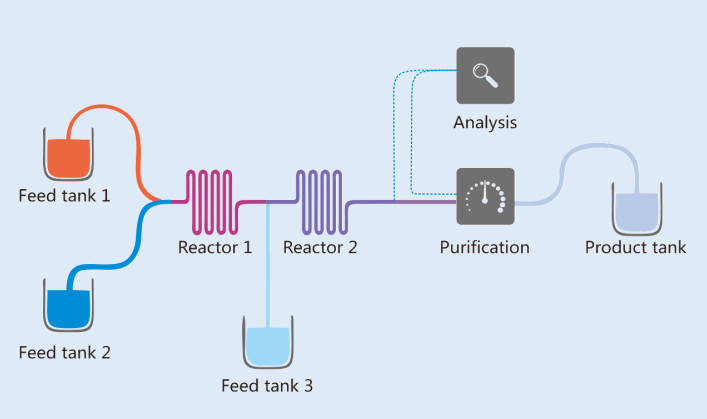
Whitepaper 【Whitepaper】Flow chemistry - An optimized solution for diazotization reaction
As an emerging technology, continuous flow chemistry is being applied in more and more reactions. On the basis of ensuring safety, the flow chemistry process can facilitate scale-up production, improve quality, and enhance time and cost-efficiency of the diazotization reaction. PharmaBlock is looking forward to expanding the application range of micro reactors in different reactions. With the increasing demand from customers, reactors of different sizes and types need to be designed and developed to accelerate pharmaceutical manufacturing. Another key point to its future will be the collaboration between AI or automated manufacturing and micro reactor technology to achieve multi-step continuous manufacturing. -
Whitepaper Application of Continuous Flow Hydrogenation with Micro-packed Bed Reactors on Manufacturing Scale
With the advancements in continuous flow technology and the ever-increasing demand for green processes, continuous flow chemistry has become more and more widely adopted in the pharmaceutical industry. The usage of micro-packed bed reactors is a viable option for application of continuous flow technology in hydrogenation. However, most of the applications are still at lab-scale. PharmaBlock will continue exploring more types of reduction transformations at manufacturing scale, and enhance the automated control systems. -
Video Innovation for Sustainability: A Dive Into ACS Green Chemistry Award-Winning Continuous Flow Manufacturing Case Studies
To improve pharmaceutical supply chain sustainability, it is crucial to place green chemistry and low-carbon technologies, including but not limited to continuous flow chemistry, and biocatalysis, at the forefront of the industry’s sustainability efforts. PharmaBlock's award-winning projects, recognized by the 2023 and 2024 ACS CMO Excellence in Green Chemistry Award, exemplify these sustainable advancements with such innovative technologies. Key discussion points include: 1. Maximizing Sustainability Returns: Enhancing the environmental performance of raw materials and RSMs is crucial for achieving the highest sustainability returns. These intermediates often have a substantial environmental footprint, as their production processes may not be as optimized as those of upstream steps, and they are produced at larger scales compared to downstream processes. 2. Overcoming Flow Technology Challenges: The application of flow technology, especially in hydrogenation and other heterogeneous reactions, presents significant challenges. These include the need for substantial investment in specialized equipment, the development of immobilized catalyst technology, and the integration of process analytical technology. 3. The environmental implications of these
Recently Visited
Position your company at the heart of the global Pharma industry with a CPHI Online membership
-
Your products and solutions visible to thousands of visitors within the largest Pharma marketplace
-
Generate high-quality, engaged leads for your business, all year round
-
Promote your business as the industry’s thought-leader by hosting your reports, brochures and videos within your profile
-
Your company’s profile boosted at all participating CPHI events
-
An easy-to-use platform with a detailed dashboard showing your leads and performance




![2,4-Dichloro-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine](https://www.cphi-online.com/46/product/70/23/40/picture.png)