Advanced Thin-Film Technique Could Deliver Long-Lasting Medication

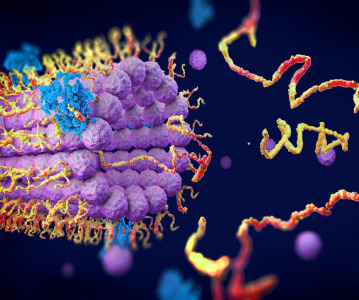
Researchers at MIT have refined a technique that could enable pain medication and other drugs to be released directly to specific parts of the body — and in steady doses over a period of up to 14 months. The method uses biodegradable, nanoscale 'thin films' laden with drug molecules that are absorbed into the body in an incremental process.
“It’s been hard to develop something that releases [medication] for more than a couple of months,” says Paula Hammond, the David H. Koch Professor in Engineering at MIT, and a co-author of a new paper on the advance. “Now we’re looking at a way of creating an extremely thin film or coating that’s very dense with a drug, and yet releases at a constant rate for very long time periods.”
In the paper, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers describe the method used in the new drug-delivery system, which significantly exceeds the release duration achieved by most commercial controlled-release biodegradable films.
“You can potentially implant it and release the drug for more than a year without having to go in and do anything about it,” says Bryan Hsu PhD ’14, who helped develop the project as a doctoral student in Hammond’s lab. “You don’t have to go recover it. Normally to get long-term drug release, you need a reservoir or device, something that can hold back the drug. And it’s typically nondegradable. It will release slowly, but it will either sit there and you have this foreign object retained in the body, or you have to go recover it.”
Layer by Layer
The paper was co-authored by Hsu, Myoung-Hwan Park of Shamyook University in South Korea, Samantha Hagerman ’14, and Hammond, whose lab is in the Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research at MIT.
The research project tackles a difficult problem in localised drug delivery: any biodegradable mechanism intended to release a drug over a long time period must be sturdy enough to limit hydrolysis, a process by which the body’s water breaks down the bonds in a drug molecule. If too much hydrolysis occurs too quickly, the drug will not remain intact for long periods in the body. Yet the drug-release mechanism needs to be designed such that a drug molecule does, in fact, decompose in steady increments.
To address this, the researchers developed what they call a “layer-by-layer” technique, in which drug molecules are effectively attached to layers of thin-film coating. In this specific case, the researchers used diclofenac, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug that is often prescribed for osteoarthritis and other pain or inflammatory conditions. They then bound it to thin layers of poly-L-glutamatic acid, which consists of an amino acid the body reabsorbs, and two other organic compounds. The film can be applied onto degradable nanoparticles for injection into local sites or used to coat permanent devices, such as orthopedic implants.
In tests, the research team found that the diclofenac was steadily released over 14 months. Because the effectiveness of pain medication is subjective, they evaluated the efficacy of the method by seeing how well the diclofenac blocked the activity of cyclooxygenase (COX), an enzyme central to inflammation in the body.
“We found that it remains active after being released,” Hsu says, meaning that the new method does not damage the efficacy of the drug. Or, as the paper notes, the layer-by-layer method produced “substantial COX inhibition at a similar level” to pills. The method also allows the researchers to adjust the quantity of the drug being delivered, essentially by adding more layers of the ultrathin coating.
A Viable Strategy for Many Drugs
Hammond and Hsu note that the technique could be used for other kinds of medication; an illness such as tuberculosis, for instance, requires at least 6 months of drug therapy.
“It’s not only viable for diclofenac,” Hsu says. “This strategy can be applied to a number of drugs.”
Indeed, other researchers who have looked at the paper say the potential medical versatility of the thin-film technique is of considerable interest.
"I find it really intriguing because it's broadly applicable to a lot of systems," says Kathryn Uhrich, a professor in the Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology at Rutgers University."
To be sure, in each case, researchers will have to figure out how best to bind the drug molecule in question to a biodegradable thin-film coating. The next steps for the researchers include studies to optimise these properties in different bodily environments and more tests, perhaps with medications for both chronic pain and inflammation.
Related News
-
News A Day in the Life of a Start-Up Founder and CEO
At CPHI we work to support Start-Up companies in the pharmaceutical industry and recognise the expertise and innovative angles they bring to the field. Through our Start-Up Programme we have gotten to know some of these leaders, and in this Day in the ... -
News Biopharmaceutical manufacturing boost part of new UK government budget
In their national budget announced by the UK Labour Party, biopharmaceutical production and manufacturing are set to receive a significant boost in capital grants through the Life Sciences Innovative Manufacturing Fund (LSIMF). -
News CPHI Podcast Series: The power of proteins in antibody drug development
In the latest episode of the CPHI Podcast Series, Lucy Chard is joined by Thomas Cornell from Abzena to discuss protein engineering for drug design and development. -
News Amgen sues Samsung biologics unit over biosimilar for bone disease
Samsung Bioepis, the biologics unit of Samsung, has been issued a lawsuit brought forth by Amgen over proposed biosimilars of Amgen’s bone drugs Prolia and Xgeva. -
News CPHI Podcast Series: Why we need to consider women in clinical trials
The latest episode of the CPHI Podcast Series with Lucy Chard covers women's health, specifically women's representation in clinical trials, the associated bias, and the impacts on health for this population. -
News US FDA does not approve MDMA therapy for PTSD, requests more data
The MDMA-based therapeutic developed by Lykos Therapeutics, a California-based Public Benefit Corporation (PBC), has been reviewed and unapproved by the US FDA. The regulator has requested additional phase III trial data for further safety and efficacy... -
News Novartis and Viatris latest facing lawsuit over HeLa cell misuse
Global pharmaceutical companies Novartis and Viatris are the latest hit with a lawsuit claim pertaining to alleged misuse of the ‘HeLa’ cell line from the estate of woman whose cancerous tissue cells were taken without consent. -
News Sanofi invests billions into Frankfurt insulin production site
French pharmaceutical company Sanofi have announced an investment of EUR1.3 billion at their existing BioCampus site in Frankfurt am Main for the expansion of insulin production.
Position your company at the heart of the global Pharma industry with a CPHI Online membership
-
Your products and solutions visible to thousands of visitors within the largest Pharma marketplace
-
Generate high-quality, engaged leads for your business, all year round
-
Promote your business as the industry’s thought-leader by hosting your reports, brochures and videos within your profile
-
Your company’s profile boosted at all participating CPHI events
-
An easy-to-use platform with a detailed dashboard showing your leads and performance


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)